What is Generative Search Optimization?
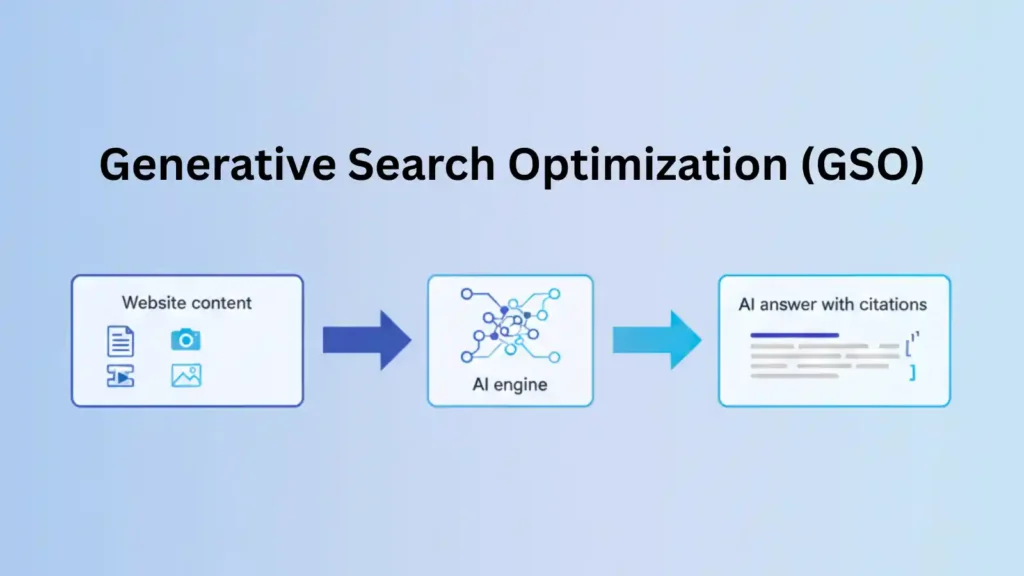
Generative Search Optimization (GSO) is the process of making your brand and content easy to comprehend, trustworthy, and “citation‑ready” for generative search experiences like Google’s AI Overviews and other AI answer engines.
You optimize so that these systems can quote you, reference your entities, and include you directly in their responses, not just compete for blue links.
To put it simply: you’re not just asking, “How do I rank my page?”
You’re asking, “How do I become the source that AI search picks to explain this topic?”
If this is your first time exploring this space, I recommend reading my full guide on AI search first:
GSO, GEO, AI search, and traditional SEO
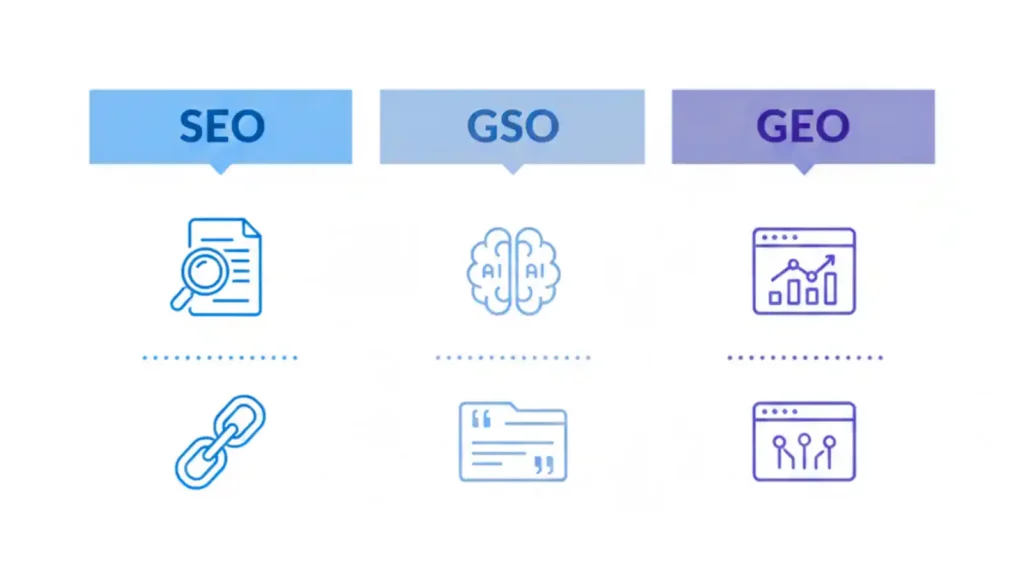
Quick comparison table
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Generative Search Optimization / GEO |
|---|---|---|
| Main objective | Rank pages in search results | Be mentioned and included in AI replies and AI Overviews |
| Primary focus | On‑page SEO, backlinks, keywords | Entities, clear writing, trust, citation‑ready content chunks |
| Query style | Short, keyword‑based queries | Questions, multi‑step prompts, conversational queries |
| Content format | Long pages and blog articles | Short answer‑first sections, tables, FAQs, structured snippets |
| Main KPIs | Rankings, organic traffic, CTR | Presence in AI panels, citations, assisted conversions |
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the tactical part of this: it means optimizing for generative engines and AI answer panels on Google and other platforms.
I’ve gone into GEO in more detail here:
If your basics aren’t strong yet, start with these foundations:
These are the building blocks that GSO uses.
How Google AI Overviews and AI search pick content
Most AI‑driven search experiences go through three steps: get, understand, and then generate.
1. Get
- They fetch pages from the web that are relevant to the topic, similar to traditional rankings.
- If your site isn’t technically sound, it usually won’t appear by default.
2. Understand
- They use entities (people, brands, products, themes) and relationships to figure out what each page is about.
- Structured data and clear headings make it easier for search engines to understand different parts of your page.
3. Generate and cite
- They put together a synthesized answer and might show citation cards or links in the AI panel.
- Short, answer‑focused sections and FAQ‑style content are much more likely to be reused.
GSO doesn’t just repeat keywords; it focuses on entities, structure, and EEAT.
Main parts of Generative Search Optimization in 2026
1. Start with entity‑based SEO
Generative engines don’t just think in strings of keywords; they think in “things” (entities) and the relationships between them.
An entity can be you, your brand, your product, your service, or a core topic like “Generative Search Optimization.”
To make entities on your site stronger:
- For each major entity (brand, service, person, core topic), create one powerful “home” page.
- Use the same names on your website, social profiles, and directory listings.
- Add Organization and Person schema with sameAs links to your real profiles.
- Use internal linking to strengthen the connections between topics and entities.
If you want to understand how entities, pillars, and clusters are related, read:
- Topic Clusters for SEO: Build Topical Authority
- Internal Linking Strategy: How to Boost Your SEO Authority
These two pieces show you exactly how to structure your site so that generative engines understand your content as a connected knowledge graph instead of separate articles.
2. Content structure that puts answers first
Generative engines want clear, direct replies they can easily take and mix into their panels.
For every significant page:
- Start with a direct answer to the main question (about 40–70 words).
- Use H2 and H3 headings that read like questions, such as “What is…?” or “How does… work?”.
- Keep paragraphs short and use bullets when you list items.
This structure is ideal for your existing pillar posts:
Putting them in an answer‑first structure can greatly improve their chances of being included in AI‑powered search results.
3. “Schema mirrors content” and structured data
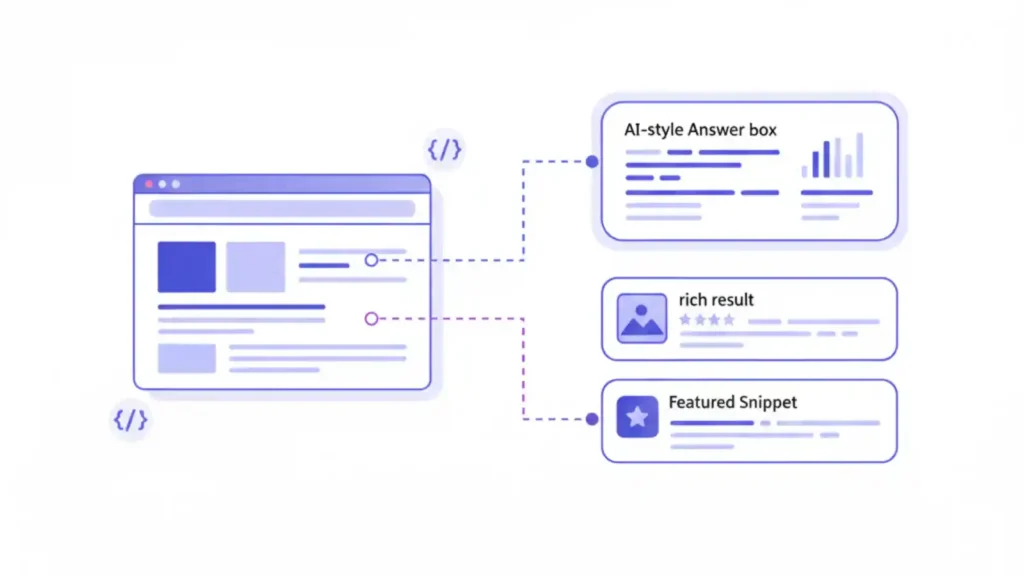
AI search engines, especially Google AI Overviews, depend heavily on structured data to understand what a page is and what questions it answers.
For GSO, focus on:
- Article / BlogPosting schema for guides like this.
- FAQPage schema for clearly separated Q&A sections.
- Organization and Person schema for your brand and author EEAT framework.
- Product or Service schema for landing pages that sell something.
If you need help implementing this, I’ve explained the essentials with examples here:
Your schema should always match the true content on the page, not phony or deceptive markup.
4. Signals of Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust (EEAT)
EEAT is now extremely important for AI‑driven search.
You can make EEAT stronger by:
- Adding detailed author profiles that show your real experience, results, and credentials.
- Including case studies and genuine examples from your client work.
- Linking to legitimate sources like Google Search Central and Google’s AI features documentation.
- Earning mentions from reliable, relevant sites in your field.
Your long‑form posts like:
act as strong authority hubs that GSO‑focused pieces can link back to.
For official references, you can safely link to:
- Google Search Central SEO Starter Guide: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/seo-starter-guide
- Google’s AI features and your website: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/ai-features
How to make Google AI Overviews work better (step by step)
Use this checklist for any page you want to appear in AI Overviews.
Step 1: Fix the essentials
- Make sure the page loads quickly, works well on mobile devices, and returns a 200 status.
- Confirm it’s indexable (no accidental noindex or blocked resources).
Step 2: Start with a clear, short answer
- Begin with a short paragraph that clearly explains the topic and gives one useful tip.
- Aim for 2–4 short sentences that could appear in a snippet.
Step 3: Sort information by intent
- Use H2s like “What is…”, “Why it matters”, “How it works”, “Steps”, “Examples”, and “FAQs”.
- Make sure each section focuses on one user need.
Step 4: Use structured data the right way
- Implement Article and FAQPage schema where it makes sense.
- Test your markup using Google’s Search Central tools.
Step 5: Add short FAQs that answer real questions
- Add 3–7 Q&As that match “People also ask” style questions.
- Mark them up with FAQPage schema and keep the answers short and clear.
Step 6: Strengthen trust and authority
- Link to official documents, including Google’s page on AI features and search.
- Build strong internal links from related posts like your AI search and GEO guides.
You can also point readers to your broader AI search guide from here:
A practical GSO framework you can use
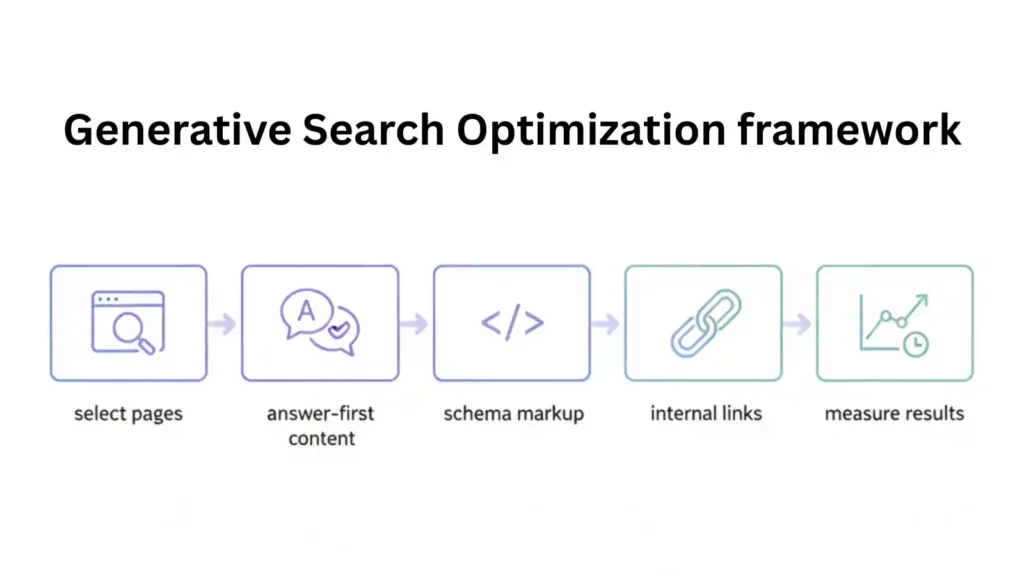
Step 1: Pick high‑impact pages
Begin with:
- Service and money pages.
- Evergreen pillar guides: WordPress SEO, on‑page SEO, AI search, GEO.
- Posts that already get traffic but don’t yet appear in AI Overviews.
For you, clear starting points are:
- WordPress SEO Optimization Guide
- On‑Page SEO Checklist
- AI Search Optimization
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Step 2: Change the format to answer‑first
On every selected page:
- Put a short, straightforward definition at the top.
- Turn the main sections into question‑based headings.
- Use bullets to break long blocks into smaller, easier‑to‑read pieces.
You’ve already used this style in posts like:
Use the same approach for your GEO and GSO sections.
Step 3: Make entities, schema, and internal links stronger
For every page:
- Make sure your name and brand are clearly visible in the content and author bio.
- Add or refine Article, FAQPage, Organization, and Person schema.
- Link from supporting posts to your pillar using descriptive anchors (for example, link “topic clusters” to your topic cluster guide).
Relevant posts you can use as supporting nodes:
- Topic Clusters for SEO
- Internal Linking Strategy
- Schema Markup Essentials
- Best SEO Tools
- SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Step 4: Add answers to FAQs and “People also ask”
Use FAQs to answer long‑tail AI queries.
For GSO pages, you can include:
- “Is Generative Search Optimization taking the place of SEO?”
- “Do I need separate content for GEO?”
- “How can I measure AI search visibility?”
Place them near the conclusion of each article and wrap them in FAQ schema.
Step 5: Refresh and measure
GSO needs regular updating.
Every three to six months:
- Update important examples, images, and statistics.
- Check which URLs show up in AI panels and which only show up in classic results.
- Use your preferred SEO tools (many of which I’ve listed in Best SEO Tools) to monitor impressions and clicks from new AI surfaces.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
You can copy this block and wrap it with FAQPage schema on your site.
Q1. What is Generative Search Optimization?
Generative Search Optimization is making your brand and content better so that AI‑powered search systems can understand, trust, and link to you directly in their replies, panels, and AI Overviews.
Q2. Is Generative Search Optimization taking the place of SEO?
No, GSO is built on traditional SEO. You still need strong technical foundations, on‑page optimization, and links, but you present information in a way that generative engines can reuse more easily.
Q3. What is the difference between GSO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GSO is a broader term for optimizing for generative search experiences, while GEO usually refers to specific strategies and techniques used to increase visibility inside generative engines and AI panels.
Q4. How can I make my site better for Google AI Overviews?
Focus on answer‑first content, clear headings, accurate schema, strong EEAT signals, and consistent internal linking within topic clusters, then monitor which pages get cited in AI panels.
Q5. How can I track how well I’m doing in AI search results?
Watch for when your URLs appear as citations in AI panels, look for changes in branded searches and assisted conversions, and compare AI‑panel visibility to standard organic rankings over time.
Q6. Do I need fresh content only for GSO?
You don’t always need brand‑new content; often, restructuring, enriching, and interlinking your best existing posts—like your AI search, GEO, schema, and topic cluster guides—is enough to start earning AI citations.



